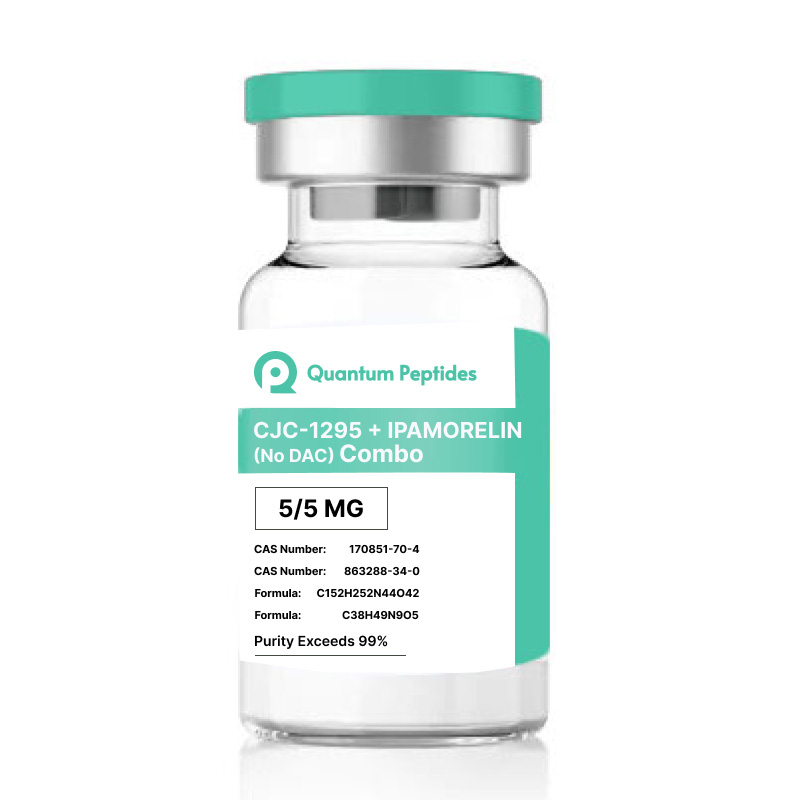
CJC-1295 & Ipamorelin Blend (10mg)
$75.00
Ipamorelin stands out as an exceptionally discerning growth hormone (GH) secretagogue, demonstrating potent agonistic activity toward the ghrelin/growth hormone secretagogue receptor. Extensively investigated across various contexts, this peptide exhibits notable effects such as enhancing bone well-being, fostering muscle repair and growth, triggering insulin release from the pancreas, and enhancing both bowel motility and gastric function. Its distinct properties make it a subject of substantial interest in scientific exploration and potential therapeutic applications.
Peptide Combination: Ipamorelin and CJC-1295
Ipamorelin and CJC-1295 peptides are recognized as growth hormone secretagogues, each with distinct structural characteristics. Ipamorelin, a synthetic pentapeptide, falls within the category of growth hormone secretagogues (GHSs), presumed to stimulate growth hormone release. While not classified as growth hormone-releasing peptides, Ipamorelin exhibits potential in influencing growth hormone secretion. On the other hand, CJC-1295, composed of 29 amino acids, is suggested to stimulate growth hormone release by mimicking the actions of natural growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH). Both peptides share a common classification, with research focusing on their similar potential effects, differing primarily in half-life and pharmacokinetic profiles.
Synergistic Potential: CJC-1295 and Ipamorelin
CJC-1295 and Ipamorelin peptides are proposed to collaborate in enhancing growth hormone levels, potentially by activating the anterior pituitary gland. Researchers theorize that this activation may lead to the natural secretion of growth hormones, thereby contributing to the sustained presence of growth hormones within the organism.
CJC-1295 peptide is a tetrasubstituted variant derived from the GHRH 1-29, designed to represent the shortest functional sequence of GHRH. This truncated peptide, consisting of the initial 29 amino acids of native GHRH, has the potential to stimulate the production of growth hormone in somatotrophs, the cells in the pituitary gland. With four strategically substituted amino acids (2nd, 8th, 15th, and 27th positions), scientists propose that these modifications enhance the peptide’s activity and resistance against proteolytic enzymes. The substituted amino acids enable covalent binding to blood albumin, potentially increasing the peptide’s half-life from 10 to 30 minutes. Consequently, this modification might lead to elevated levels of plasma growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1).
CJC-1295 may be associated with a potential drug affinity complex (DAC) component that binds to plasma proteins. This DAC element in CJC-1295 refers to the attachment of N-epsilon-3-maleimidopropionamide derivative of lysine at the C-terminal end. The integration of the tetrasubstituted amino acid chain and the DAC element seems to result in improved pharmacokinetics while maintaining a comparable affinity to GHRH receptors in the pituitary gland, similar to natural GHRH. Researchers emphasize that during the peptide’s “selection for further pharmacokinetic evaluation, it demonstrated a presence in plasma for over 72 hours.”
Ipamorelin, also recognized as NNC 26-0161, is a synthetically created pentapeptide believed to interact with the growth hormone secretagogue receptor (GHS-R1a) in pituitary gland cells. These receptors, predominantly located in the hypothalamus, are commonly known as ghrelin receptors due to their association with ghrelin, a natural ligand. Ipamorelin distinguishes itself among other growth hormone secretagogues (GHSs) for its potential selectivity, which may lead to the stimulation of growth hormone (GH) release by somatotroph cells without a concurrent increase in other hormones produced by the anterior pituitary gland, such as prolactin.
When administered together as a peptide combination, often referred to as the peptide stack, research studies consistently indicate that Ipamorelin demonstrates its primary effects in the initial stages, manifesting noticeable impacts within the first two hours of administration. Subsequently, as the effects of Ipamorelin begin to diminish, the CJC-1295 peptide tends to gradually complement and sustain the overall action of the blend.
Studies and Clinical Investigations
Blend of CJC-1295 and Ipamorelin Peptides: Determination of Half-Life and Pharmacokinetic Profiles
Clinical investigations have been undertaken involving subjects to ascertain the half-life and individual pharmacokinetic characteristics of the CJC-1295 and Ipamorelin peptides. In a clinical trial conducted in the late 1990s, eight male subjects participated in a concentration escalation study, with growth hormone levels monitored after each peptide administration. The study’s findings suggested a single episode of growth hormone release, reaching its highest peak at 0.67 hours, followed by an exponential decline to negligible concentrations. The conclusion indicated that Ipamorelin exhibited a short half-life of approximately 2 hours, after which its potential effects began to diminish.
On the contrary, CJC-1295 exhibits a notably extended half-life. Researchers suggest that a single administration of the peptide may stimulate sustained growth hormone production by somatotrophs, contributing to an overall increase in growth hormone secretion by approximately 46%. Additionally, there is a potential upregulation of its primary anabolic mediator, insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), by an average of 45%. Another study notes that CJC-1295 could potentially elevate growth hormone concentrations by 2- to 10-fold, estimating a half-life ranging between 5.8 – 8.1 days.
CJC-1295 & Ipamorelin Combination: Comprehensive Investigation
In a clinical investigation conducted in the early 2000s, male participants within the age range of 20 to 40 were enrolled in a study, with one group administered a placebo and the other presented with the CJC-1295 peptide. Blood samples were collected a week prior to and after the administration of the peptide (and placebo) to assess the fluctuations in growth hormone pulsatility. The findings indicated a noteworthy 7.5-fold increase in growth hormone pulsatility levels attributable to CJC-1295 compared to the placebo. Beyond influencing growth hormone synthesis, researchers propose that CJC-1295 may interact with the survival and proliferation of somatotroph cells in the anterior pituitary gland. A murine model study aligned with these findings, highlighting an increase in total pituitary RNA and GH mRNA, suggesting potential somatotroph cell proliferation, as affirmed by immunohistochemistry images.
Conversely, Ipamorelin seems to engage with cells in the anterior pituitary gland through the N-terminus of GHS-R1a, where binding sites recognize specific sequences within the secretagogue. Upon encountering this receptor, Ipamorelin may temporarily attach through interactions like hydrogen bonds and van der Waals forces between molecules. This attachment could induce a change in the receptor’s shape, initiating cell signals, particularly those involving G-proteins. GHS-R1a is thought to collaborate with a specific segment of G-proteins known as Gαq/11. A pivotal process initiated by GHS-R1a involves the enzyme phospholipase C (PLC). Gαq/11 interacts with PLC, leading to the breakdown of a lipid-like molecule, phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2), into two signaling molecules: IP3 (Inositol trisphosphate) and DAG (Diacylglycerol). IP3 attaches to sites on a cell structure called the endoplasmic reticulum, triggering the release of calcium ions (Ca2+). Additionally, DAG activates an enzyme known as protein kinase C (PKC), facilitating the addition of phosphate groups to other signaling molecules. This series of events culminates in the activation of proteins that aid in the release of growth hormone from specific cells in the pituitary gland.
The cooperative influence of CJC-1295 and Ipamorelin on growth hormone production in the somatotroph cells of the anterior pituitary gland appears to contribute to a positive nitrogen balance and a potential increase in lean mass in experimental models. In a specific investigation, researchers aimed to explore the metabolic effects of Ipamorelin, focusing on hepatic markers related to alpha-amino-nitrogen processing during artificially induced catabolism. The study assessed the liver’s capacity to generate urea-N (CUNS), serving as a potential indicator of nitrogen processing in the liver. Analysis included the examination of mRNA levels associated with enzymes of the urea cycle in the liver, evaluation of overall nitrogen balance, and estimation of nitrogen quantities in various organs. The findings suggested that Ipamorelin might have resulted in a 20% reduction in CUNS compared to the artificially induced catabolic condition. Additionally, it potentially decreased the expression of urea cycle enzymes, restored nitrogen balance, and theoretically adjusted or improved nitrogen values in organs.
The CJC-1295 & Ipamorelin peptide combination is exclusively intended for research and laboratory applications. Prior to placing an order, it is imperative to carefully review and comply with our Terms and Conditions. These peptides are not intended for any use beyond scientific research, and adherence to ethical and legal guidelines is essential.




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.